

Next: Neurophysiological Observations
Up: Lateral Facilitation and
Previous: Lateral Facilitation and
Psychophysically, the visibility of a small foveally
viewed Gabor patch can either be enhanced or suppressed by laterally placed Gabor patches of
similar orientation and spatial frequency. The sign of the effect, enhancement or suppression,
depends on target and flank separation and on the relative orientation of the target and its
flanks. Maximal threshold enhancement occurs for co-oriented, collinear targets that are
separated by several wavelengths of the spatial frequency of the Gabor patches.
The changes in contrast threshold, relative to a standard (no mask) condition is plotted
in Figure 1 as a function of target to mask distance (in units of target wavelength).
Two zones, suppression and facilitation, where contrast
detection thresholds are affected by flanking Gabor maskers were observed.
The suppression region, within an eccentricity of 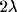 ,
contrast detection thresholds increased up to factor of two. Outside this region detection
thresholds are reduced up to factor of two, resulting in a facilitatory region extended up
to
,
contrast detection thresholds increased up to factor of two. Outside this region detection
thresholds are reduced up to factor of two, resulting in a facilitatory region extended up
to 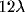 . Maximum facilitation found at
. Maximum facilitation found at 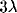 and progressively returning to the standard
threshold by
and progressively returning to the standard
threshold by 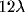 .
Assuming a filter size of about 2 wavelengths (e.g.
[41]), facilitatory
effects occurred over distances spanning several receptive fields.
Suppression had a much shorter spatial range
and presumably was due to interactions from nearby filters
[43].
.
Assuming a filter size of about 2 wavelengths (e.g.
[41]), facilitatory
effects occurred over distances spanning several receptive fields.
Suppression had a much shorter spatial range
and presumably was due to interactions from nearby filters
[43].
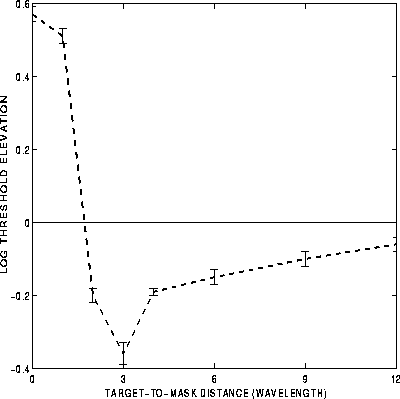
Figure 1: Dependence of target perceptual threshold on target to mask distance.
Threshold elevation is computed relative to that of an isolated target.
Data is presented for a collinear configuration of target and masks (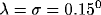 ).
Similar functions are found for
different target and mask spatial frequencies.
).
Similar functions are found for
different target and mask spatial frequencies.


Next: Neurophysiological Observations
Up: Lateral Facilitation and
Previous: Lateral Facilitation and
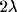 ,
contrast detection thresholds increased up to factor of two. Outside this region detection
thresholds are reduced up to factor of two, resulting in a facilitatory region extended up
to
,
contrast detection thresholds increased up to factor of two. Outside this region detection
thresholds are reduced up to factor of two, resulting in a facilitatory region extended up
to 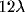 . Maximum facilitation found at
. Maximum facilitation found at 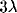 and progressively returning to the standard
threshold by
and progressively returning to the standard
threshold by 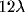 .
Assuming a filter size of about 2 wavelengths (e.g.
[41]), facilitatory
effects occurred over distances spanning several receptive fields.
Suppression had a much shorter spatial range
and presumably was due to interactions from nearby filters
[43].
.
Assuming a filter size of about 2 wavelengths (e.g.
[41]), facilitatory
effects occurred over distances spanning several receptive fields.
Suppression had a much shorter spatial range
and presumably was due to interactions from nearby filters
[43].



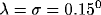 ).
Similar functions are found for
different target and mask spatial frequencies.
).
Similar functions are found for
different target and mask spatial frequencies.